Did you know that the debilitating childhood disease rickets is making a comeback in the world? Especially in western countries like England and the U.S.? Or that our children are suffering from more and more autoimmune diseases at earlier and earlier ages? Do you know why? It isn’t because of pollution, it isn’t because of poverty, it isn’t really even due a lack of lack of vitamin D in the diet. Its a lack of sun exposure. For the most part, our children aren’t being forced into dark factories like in previous generations, those factories aren’t spewing out black soot blocking the sun, there isn’t rampant disease causing parents to keep children off the streets. The cause is a largely unfounded and irrational fear of skin cancer. Often times Vitamin D deficiency shows up in infants because the baby’s mother is Vitamin D deficient and the baby is breastfed (PubMed #PMC3012634). Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency are increasingly common in western cultures.
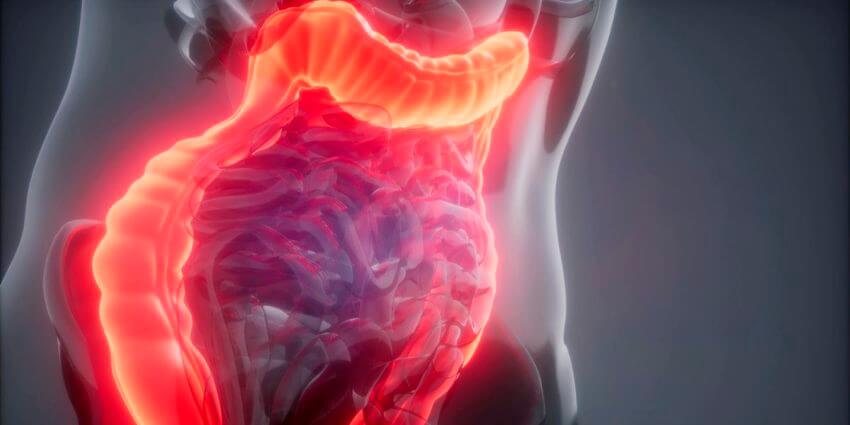
It is clear from the studies (below) that Vitamin D insufficiency is directly related to inflammation and poor mucosal barrier function. Both of these have a direct impact on the gut and gut related diseases such as SIBO. Vitamin D is so important to the immune system that some bacteria actually inhibit our body’s ability to absorb and utilize Vitamin D, doing this for their own survival.
“Over the past decade, numerous studies have shown that many Americans have low vitamin D levels and as a result, vitamin D supplement use has climbed in recent years. Vitamin D has been shown to boost bone health and it may play a role in preventing diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease and other illnesses. In light of the increased use of vitamin D supplements, Mayo Clinic researchers set out to learn more about the health of those with high vitamin D levels. They found that toxic levels are actually rare…We found that even in those with high levels of vitamin D over 50 ng/mL, there was not an increased risk of hypercalcemia, or elevated serum calcium, with increasing levels of vitamin D” — Mayo Clinic Proceedings, summary (full text)
“VDR (Vitamin D Receptor) signaling on immune function has been the focus of many recent studies as a link between 1,25(OH)2D3 and susceptibility to various infections and to development of a variety of inflammatory diseases has been suggested. It is also becoming increasingly clear that microbes slow down immune reactivity by dysregulating the VDR ultimately to increase their chance of survival.” — PubMed #PMC3684798
Besides getting enough Vitamin D, it is also important to be able to utilize it. A very small minority of people are born with a defective in the CYP27B1 gene that codes for VDR (Vitamin D Receptor). In the elderly mitochondrial dysfunction can cause CYP27B1 to not function properly. But what is most fascinating is the thought that some microbes may have the ability to interfere with vitamin D utilization by dysregulating VDR. This would not only protect the microorganism but cause additional diseases to take hold, even making someone much more susceptible to the flu. However, it may be possible to overcome VDR dysregulation in some cases by increasing Vitamin D intake (PubMed #PMC2553887) to compensate.
“VDR plays a critical role in mucosal barrier homeostasis by preserving the integrity of junction complexes and the healing capacity of the colonic epithelium. Therefore, vitamin D deficiency may compromise the mucosal barrier, leading to increased susceptibility to mucosal damage and increased risk of IBD…D3 markedly enhanced tight junctions formed by Caco-2 monolayers by increasing junction protein expression and TER and preserved the structural integrity of tight junctions” — PubMed #17962355
“Our recent studies unveil a regulatory circuit that centers gut epithelial VDR as a key molecule in the control of mucosal inflammation and colitis development. On the one hand, intestinal epithelial VDR signaling protects the integrity of the mucosal barrier by inhibiting inflammation-induced epithelial cell apoptosis. This barrier-protecting, anti-colitic activity is independent of the non-epithelial immune VDR actions. A healthy and intact mucosal barrier prevents bacterial invasion and thus reduces mucosal inflammation. On the other hand, inflammation in turn down-regulates epithelial VDR expression by inducing VDR-targeting microRNA-346, thus compromising mucosal barrier functions. Consistently, colonic epithelial VDR levels are markedly reduced in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases or in experimental colitis models, whereas vitamin D analog therapy that ameliorates colitis up-regulates epithelial VDR. Thus, gut epithelial VDR signaling appears to play an essential role in controlling mucosal inflammation and thus could be a useful therapeutic target in the management of inflammatory bowel diseases.” — PubMed #25603468
If the bacteria are preventing Vitamin D utilization we won’t be able to repair the mucosal barrier, thus allowing for a worsening of the infection and perhaps secondary infections. All of this leads to mucosal inflammation and leaky gut. As the following study indicates poor Vitamin D levels also affects the Tight Junctions, which prevent bacteria and proteins from crossing through the small intestine into the bloodstream (leaky gut).
“The anti-inflammation and anti-infection functions for Vitamin D are newly identified and highly significant activities. Vitamin D/VDR have multiple critical functions in regulating the response to intestinal homeostasis, tight junctions, pathogen invasion, commensal bacterial colonization, antimicrobe peptide secretion, and mucosal defense. Interestingly, microorganisms modulate the VDR (Vitamin D Receptor) signaling pathway.” — PubMed #PMC2955835
“Many studies have implicated Vitamin D and VDR in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Low Vitamin D levels have been reported in patients with IBD. The VDR protein is significantly lower in IBD and colitis-associated colon cancer patients… It has also been shown that VDR stabilizes cell tight junction structures in the intestinal epithelial cells; hence, proper functioning of VDR is needed to control intestinal homeostasis…Consistent with its anti-inflammatory role, 1,25(OH)2D3 downregulates the expression of many proinflammatory cytokines…. Cells of the gastrointestinal tract, including epithelial cells and lamina propria macrophages, are constantly exposed to lumenal bacteria, which play key roles in normal intestinal development and innate immunity. The intestinal Paneth cells are known to secrete antimicrobial peptides, which are regulated by VDR signaling.” — PubMed #PMC2955835
“The involvement of Vitamin D/VDR in anti-inflammation and anti-infection represents a newly identified and highly significant activity for VDR. Studies have indicated that the dysregulation of VDR may lead to exaggerated inflammatory responses, raising the possibility that defects in Vitamin D and VDR signaling transduction may be linked to bacterial infection and chronic inflammation.” — PubMed #20639756
Have you ever wondered why the cold and flu are more common in the winter? It isn’t because we congregate together more in the winter, most of us now work indoors all year round.
“In 1981, R. Edgar Hope-Simpson proposed that a ‘seasonal stimulus’ intimately associated with solar radiation explained the remarkable seasonality of epidemic influenza. Solar radiation triggers robust seasonal vitamin D production in the skin; vitamin D deficiency is common in the winter… 1,25(OH)2D acts as an immune system modulator, preventing excessive expression of inflammatory cytokines and increasing the ‘oxidative burst’ potential of macrophages. Perhaps most importantly, it dramatically stimulates the expression of potent anti-microbial peptides, which exist in neutrophils, monocytes, natural killer cells, and in epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract where they play a major role in protecting the lung from infection… An interventional study showed that vitamin D reduces the incidence of respiratory infections in children. We conclude that vitamin D, or lack of it, may be Hope-Simpson’s ‘seasonal stimulus’.” — PubMed #16959053
“The data support the hypothesis that a high vitamin D level, as that found in the summer, acts in a protective manner with respect to influenza as well as pneumonia.: — PubMed #PMC3092571
“Deficiency in vitamin D is associated with increased autoimmunity as well as an increased susceptibility to infection. As immune cells in autoimmune diseases are responsive to the ameliorative effects of vitamin D, the beneficial effects of supplementing vitamin D deficient individuals with autoimmune disease may extend beyond the effects on bone and calcium homeostasis…The implications of vitamin D deficiency on the immune system have become clearer in recent years and in the context of vitamin D deficiency, there appears to be an increased susceptibility to infection and a diathesis, in a genetically susceptible host to autoimmunity” — PubMed #PMC3166406
“One report studied almost 19,000 subjects between 1988 and 1994. Individuals with lower vitamin D levels (<30 ng/ml) were more likely to self-report a recent upper respiratory tract infection than those with sufficient levels” — PubMed #PMC3166406
“type 1 diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis (MS), and inflammatory bowel disease has been linked to geographic location with a higher incidence of these diseases at higher degrees of latitude. One explanation of this geographical distribution is low exposure to sunlight and hence lower levels of vitamin D” — PubMed #PMC3684798
“Recently, important progress has been made in understanding how the noncanonical activities of Vitamin D influence the pathogenesis and prevention of human disease. Vitamin D and VDR are directly involved in T cell antigen receptor signaling. The involvement of Vitamin D/VDR in anti-inflammation and anti-infection represents a newly identified and highly significant activity for VDR. Studies have indicated that the dysregulation of VDR may lead to exaggerated inflammatory responses, raising the possibility that defects in Vitamin D and VDR signaling transduction may be linked to bacterial infection and chronic inflammation.” — PubMed #PMC2955835
“low 25(OH)D concentrations were associated with serum markers of inflammation that are indicators of cardiac risk.” — PubMed #PMC3012634
“A number of studies have suggested that patients with autoimmune diagnoses are deficient in 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-D) and that consuming greater quantities of vitamin D, which further elevates 25 D levels, alleviates autoimmune disease symptoms… the Vitamin D nuclear receptor (VDR) affects transcription of at least 913 genes…symptomatic improvements among those administered vitamin D is the result of 25-D’s ability to temper bacterial-induced inflammation” — Pubmed #19393200
“The VDR is nearly ubiquitously expressed, and almost all cells respond to 1,25-(OH)2D exposure; about 3% of the mouse or human genome is regulated, directly and/or indirectly, by the vitamin D endocrine system… The immune system of VDR- or vitamin D-deficient mice is grossly normal but shows increased sensitivity to autoimmune diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease or type 1 diabetes after exposure to predisposing factors… Vitamin D deficiency in humans is associated with increased prevalence of diseases… ” — PubMed #PMC2583388
Lower Mortality Rates:
“In a prospective observational study of adults older than 65 years participating in NHANES III, the risk of death was 45% lower in those with 25(OH)D values greater than 40 ng/mL compared with those with values less than 10 ng/mL” — PubMed #PMC3012634
“In noninstitutionalized older adults, a group at high risk for all-cause mortality, serum 25(OH)D levels had an independent, inverse association with CVD and all-cause mortality. Randomized controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation in older adults are warranted to determine whether this association is causal and reversible.” — PubMed #19549021
“Low 25(OH)D levels are associated with all-cause mortality and even more pronounced with cardiovascular mortality” — PubMed #19226272
“Ecological and observational studies suggest that low vitamin D status could be associated with higher mortality from life-threatening conditions including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes mellitus that account for 60% to 70% of total mortality in high-income countries. We examined the risk of dying from any cause in subjects who participated in randomized trials testing the impact of vitamin D supplementation… Intake of ordinary doses of vitamin D supplements seems to be associated with decreases in total mortality rates.” — PubMed #17846391
Now that they’ve shown that it is very difficult to overdose on Vitamin D and that even among people with high blood levels (over 80ng/ml) hypercalcemia, and other side effects, are very rare — Mayo Clinic News Release there really is no reason not to supplement to get your blood levels up to the optimal 50-60 ng/ml.
The sun is the preferred source of Vitamin D. If you burn easily you can greatly enhance your ability to avoid sunburn (and enjoy more time outdoors!) by doing the following:
- Avoid polyunsaturated fats (PUFA) as much as possible, replace with unsaturated (olive oil) and saturated fats (coconut oil, palm oil, butter and other animal fats)
- Improve your Omega 6:Omega 3 ratio. Largely accomplished by reducing PUFAs. Consuming fish, fish oil tablets, and a DHA supplement will also help.
- Take a astaxanthin supplement daily, at least 4mg / day, 8mg is better, especially in the summer months.
- Supplement with 8-10 grams of glycine per day and/or consume bone broths daily. Glycine is very protective of UV radiation damage and inflammation.
- Take a Vitamin D supplement. Vitamin D is protective of UV damage.
- Caucasians – Tan. Once you’ve added the above to your diet you should be able to get a tan quite easily. Start off slowly. 30 minutes the first day. Waits 48 hours and see what happens. If all is well try an hour the next time. Increase as desired. (non-caucasians with dark skin need more sun than light skinned people. The good news is that it’s harder for your to burn)
I myself use to literally get burned (I mean beet red, peeling, and blisters) after 15-20 minutes of sun exposure! I’m talking late March in Minnesota sun exposure!! Now I can stay out almost all day in August! This is probably one of the most dramatic and visible things I’ve done for my health. Cancer is believed to be caused by sunburns, not sun exposure. It is easy to confuse the two, but if you don’t burn, you don’t get those deep sunburns that cause cancer.
My wife and I both take 5,000 IU’s of vitamin D per day; year round on days we don’t get enough from the sun. During January and February we sometimes increase this to 10,000 IU’s. Once summer hits we try to spend as much time outside getting as much sun as possible (especially midday sun). We sometimes use coconut oil or an SPF 15 sunscreen on our faces after they’ve had an hour or so of exposure. This is more to prevent skin aging than anything else. Our Vitamin D supplement also contains Vitamin K2 so that the enhanced calcium absorption facilitated by Vitamin D gets utilized the way it should, to rebuild the bones and teeth. I also consume an additional K2 supplement as I believe that it also helps with repairing the small intestine. See “Vitamin K2 and the Calcium Paradox” by Kate Rheaume-Bleue. Both of these supplements can be found in the Amazon Store but as always, purchase it where ever you can find it cheapest.
All images posted by John Herron are either "Copyrighted John Herron", or are copyrighted by someone else and are used under license. So please don’t use them elsewhere, you’ll get in trouble.

 Phage Complete comes with a full 30 day money back guarantee, for U.S. purchases this includes the original shipping charges to you!
Phage Complete comes with a full 30 day money back guarantee, for U.S. purchases this includes the original shipping charges to you!
There is an alternative view. It may be that large scale supplementation of vitamin D among the young in much of the developed world is leading to more allergies and more digestive diseases. In fact some evidence suggests that oral vitamin D supplementation among the young may increase the probability of developing celiac disease in later life. Here is a journal article that I wrote on this topic: http://www.hoajonline.com/journals/pdf/2054-9873-2-2.pdf.
i have leaky gut and candida, took 10,000 iu daily with no noticeable results, and recently upped it to 50,000 iu daily plus magnesium and K and within 4 days, my mucous levels WAY down, my hair stopped falling out and my stomach doesn’t hurt anymore. just so you know….
Thank you, good information. You probably would have eventually felt better with 10,000 IU/day but you speed up the process. Good call on teaming it up with the magnesium and Vitamin K2! For other people reading this, you probably should know your Vitamin D levels before starting. If they’re good (e.g. >45ng/ml, 60ng/ml probably being about optimal), your problem may be something else.
Hi Michelle, this is months later so I am not sure you will see this, but, I have also been diagnosed with Candida. Did you check your vitamin D levels and were you ever “over” the limit…did you eventually stop taking the 50,000?
Tami,
The Mayo Clinic recently did a study on Vitamin D toxicity and found it to be very rare. Most experts say that we should try to keep our levels below 100 ng/ml which appears to be the average maximum we can obtain from sunlight alone.
“We found that even in those with high levels of vitamin D over 50 ng/mL, there was not an increased risk of hypercalcemia, or elevated serum calcium, with increasing levels of vitamin D,”
“The evidence is clear that vitamin D toxicity is one of the rarest medical conditions and is typically due to intentional or inadvertent intake of extremely high doses,” writes Hollick, a professor of medicine, physiology and biophysics at Boston University School of Medicine.
– MayoClinic.org
If you have Candida, especially with intestinal issues, you should visit our Facebook group “The Gut Health Protocol”; the book of the same name discusses some very effective natural treatments for it.
Effects of high doses of vitamin D3 on mucosa-associated gut microbiome vary between regions of the human gastrointestinal tract
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4875045/
Interesting paper on the topic.
Worth reading this paper as well to better understand why DAILY CHOLECALCIFEROL (half life 24hrs) may improve matters.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4607301/
Dietary Vitamin D and Its Metabolites Non-Genomically Stabilize the Endothelium
I have Sibo c and nothing helps .Now I will try vitamin D.I lost 10 kg in the last year.Now my weight is 44 kg!! I hope, my resorption will be better. Thanks for this interesting articles.